WWI toxic compound sprayed on Georgian protesters, BBC evidence suggests
Published: 30 November 2025
By Max Hudson, Oana Marocico and Sarah Buckley
via the BBC website
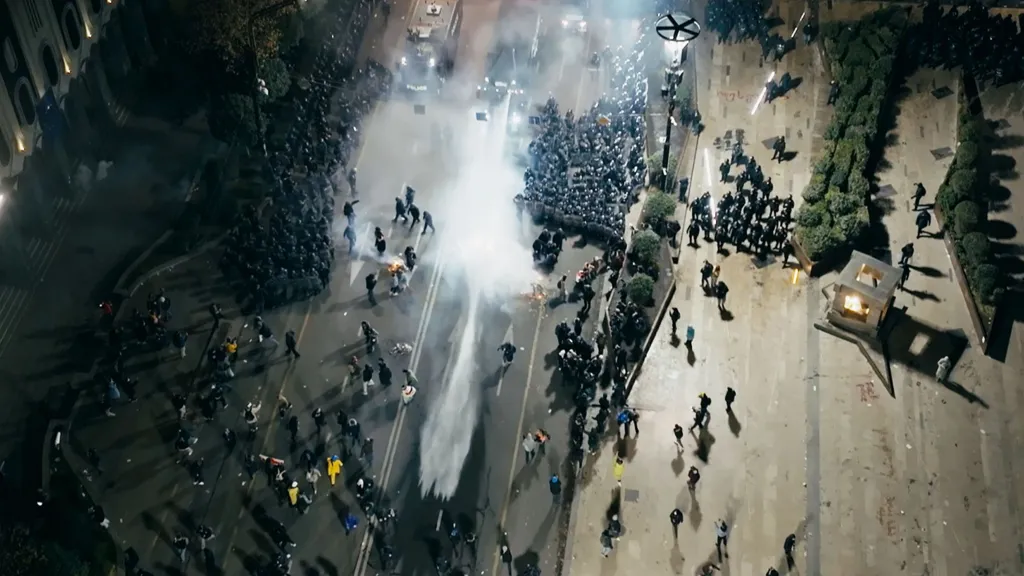
Georgia protestors
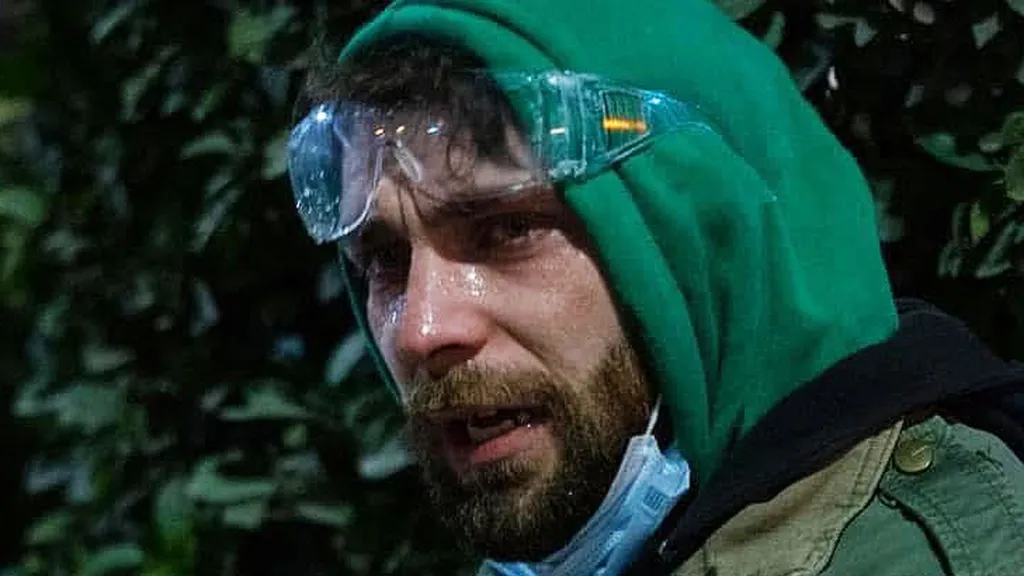
Protesters against the Georgian government have complained of long-lasting symptoms after being sprayed by water cannon (Shutterstock)
Georgia’s authorities used a World War One-era chemical weapon to quell anti-government protesters last year, evidence gathered by the BBC suggests.
“You could feel [the water] burning,” one of the protesters said of water cannon turned on him and others on the streets of the capital Tbilisi. A sensation, he said, which could not immediately be washed off.
Demonstrators against the Georgian government’s suspension of its European Union accession bid have complained of other symptoms too – shortness of breath, coughing, and vomiting that lasted for weeks.
The BBC World Service has spoken to chemical weapons experts, whistleblowers from Georgia’s riot police, and doctors, and found the evidence points to the use of an agent that the French military named “camite”.
The Georgian authorities said our investigation findings were “absurd” and the police had acted legally in response to the “illegal actions of brutal criminals”.
Camite was deployed by France against Germany during World War One. There is little documentation of its subsequent use, but it is believed to have been taken out of circulation at some point in the 1930s, because of concerns about its long-lasting effects. CS gas – often referred to as “tear gas” – was used as a replacement.
Konstantine Chakhunashvili was one of those who gathered outside Georgia’s parliament in Tbilisi during the first week of protests – which began on 28 November 2024. Demonstrators were incensed by the ruling party’s announcement that it was pausing EU accession talks. The goal of EU membership is enshrined in Georgia’s constitution.
⇒ Read the entire article on the BBC website.
External Web Site Notice: This page contains information directly presented from an external source. The terms and conditions of this page may not be the same as those of this website. Click here to read the full disclaimer notice for external web sites. Thank you.




