Honoring World War I “Balloon Buster” Frank Luke Jr.
Published: 13 February 2023
By Thomas Paone
via the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum web site
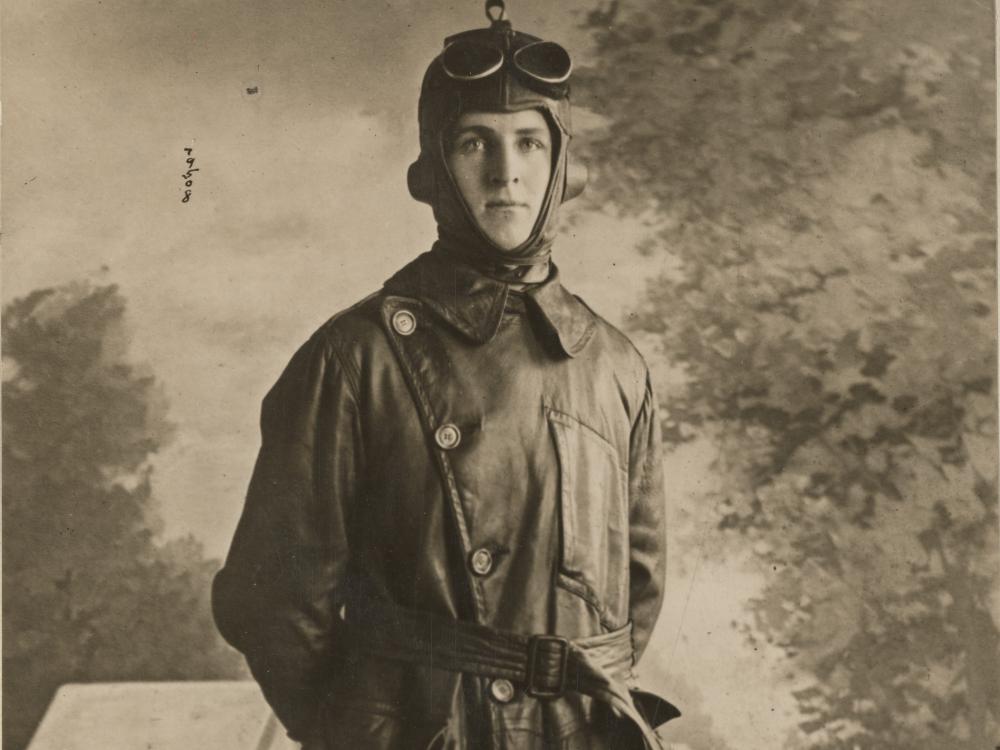

Frank Luke, Jr
The Historical Thread Connecting a Balloon over the United States to the Skies above World War I Europe
On February 6, 2023, Gen. Glen VanHerck, the commander of North American Aerospace Defense Command and U.S. Northern Command, participated in a press conference that provided updates regarding the American destruction of a Chinese high-altitude balloon flying over the United States. Buried within details about the ongoing investigations and information about countermeasures, a question arose about whether or not the F-22 that shot down the balloon would receive a decal to signify the air-to-air victory, as is traditional for pilots. General VanHerck deferred that decision to the leaders of the fighter wing, but did mention an important aspect of the mission that directly tied it to aerial combat of the past:
“I will say I’m really incredibly proud of everybody that took place in this. But the F-22 was remarkable. I’d remind everybody that the call sign of the first flight was Frank 01 … [named for] Frank Luke, [a] Medal of Honor winner [in] World War I for his activities that he conducted against observation balloons. So how fitting is it that Frank 01 took down this balloon in sovereign airspace of the United States of America within our territorial waters.”

Frank Luke Jr. in his flight gear. (Image courtesy of the National Archives and Records Administration, 65-WW-433P-1631)
Who was Frank Luke?
Frank Luke Jr. was an American pilot from Phoenix, Arizona, whose short but impressive air combat career made him one of the top “balloon busters” of World War I. Luke was, by many accounts, a naturally talented pilot who struggled at times with the discipline found in the military command structure.
Starting in August 1918, Luke flew with the 27th Aero Squadron of the 1st Pursuit Wing, conducting solo patrol missions along the front. September 1918, however, brought Luke into contact with observation balloons along the German front lines, and he showed an incredible talent for shooting them down.
Although the large, tethered observation balloons may seem like an easy target for a talented pilot, attacking them was incredibly risky and difficult. Observation balloons were a critical component of combat during World War I, providing “eyes in the sky” for commanders and watching the movements of the enemy when they were airborne.
Observers in balloons could also communicate with commanders on the ground and adjust artillery fire in real time, adding deadly accuracy to a barrage. These factors made them a prime target for pilots, as the elimination of a barrage balloon greatly hindered the offensive and defensive capabilities of the enemy.
The importance of barrage balloons, however, also meant they were heavily defended. Balloons were often surrounded with numerous anti-aircraft guns. Pursuit planes were also often assigned to protect the balloons, so any pilot brave enough to make an attack on a balloon may find numerous enemy planes in the air ready to protect the balloon at all costs. These numerous layers of defense make Luke’s career even more remarkable.
Between September 12 and September 29, 1918, Luke shot down a total of 14 observation balloons. During an attack on September 29, Luke brought down three enemy observation balloons in under 45 minutes, an incredible feat considering the defenses he faced. This feat, however, came at the ultimate cost for Luke. Shortly after destroying the third balloon, Luke was brought down by one of the anti-aircraft positions near the balloon, leading to his death.
Luke had a total of 19 confirmed aerial victories at the time of his death, including both enemy balloons and aircraft, making him one of the top U.S. aces of the war. Luke was awarded the Distinguished Flying Cross twice for his actions and was posthumously awarded the Medal of Honor, becoming the first United States pilot to receive the honor in the war.
Read the entire article on the National Air and Space Museum web site.
External Web Site Notice: This page contains information directly presented from an external source. The terms and conditions of this page may not be the same as those of this website. Click here to read the full disclaimer notice for external web sites. Thank you.